We put research into practice
Innovation is more than a buzzword for us. Equipped with our own research institute and thanks to strong research collaborations, we do not only implement innovative technologies into our practices as fast as possible, but we also test their efficiency in treatment.
Research goals
The goal of our research and partnerships is to develop a novel form of neurorehabilitation that is seamlessly integrated into the daily routine of our patients. The goal is that you train yourself by being as active as possible. The necessary corrective feedback, assistance and safety measures are provided by intelligent technology and by the interaction with your therapist.
We are continuously taking part in innovative research collaborations and projects working in conjunction with renowned educational bodies around the world and always aiming for the highest quality of neurorehabilitation, based on the latest scientific developments.
Motivation
Patients need to be self-motivated to be active in their daily lives. Our motivational research focuses on innovative therapy approaches to incentivise and foster active training and activity in everyday life.
Taking ownership
We are continuously taking part in innovative research collaborations and projects working in conjunction with renowned educational bodies around the world and always aiming for the highest quality of neurorehabilitation, based on the latest scientific developments.
Research collaborations
The latest technology in stroke recovery
Our neurorehabilitation clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art movement analysis, robotic systems and other innovative devices to complement the hands-on training with the therapist.
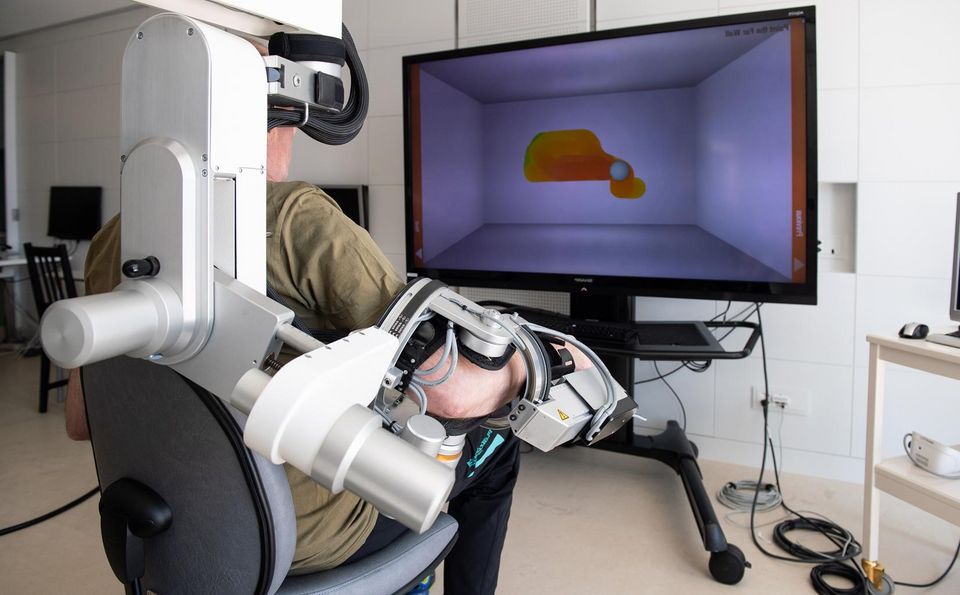
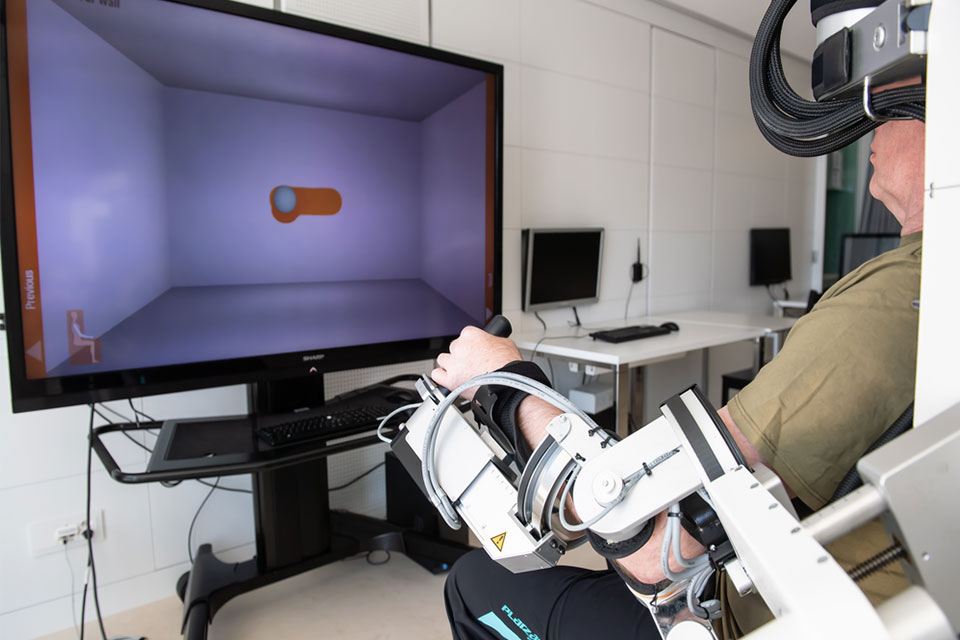
Armeo® Power by Hocoma
This arm exoskeleton helps impaired patients to train their arm movement by assisting with force.
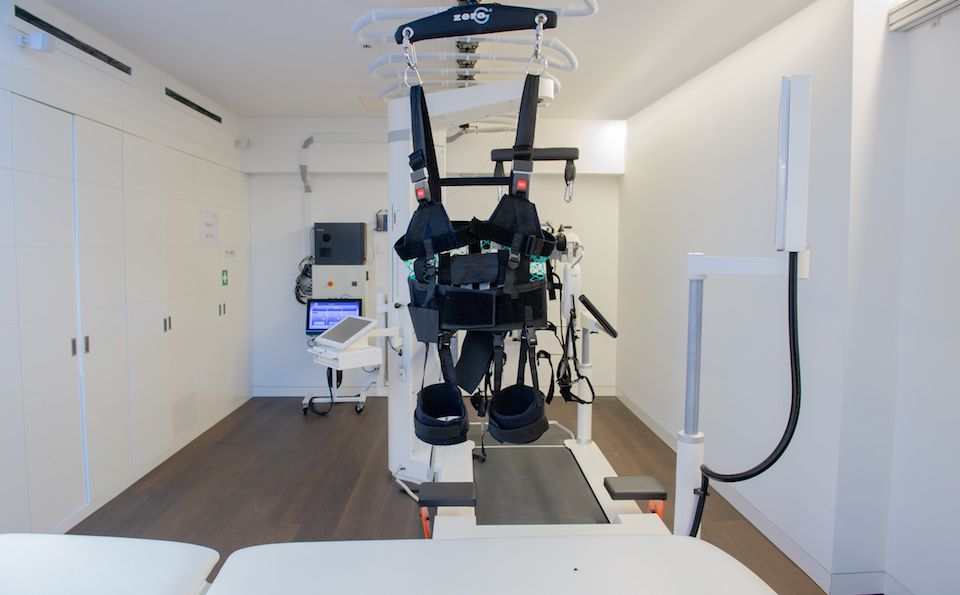
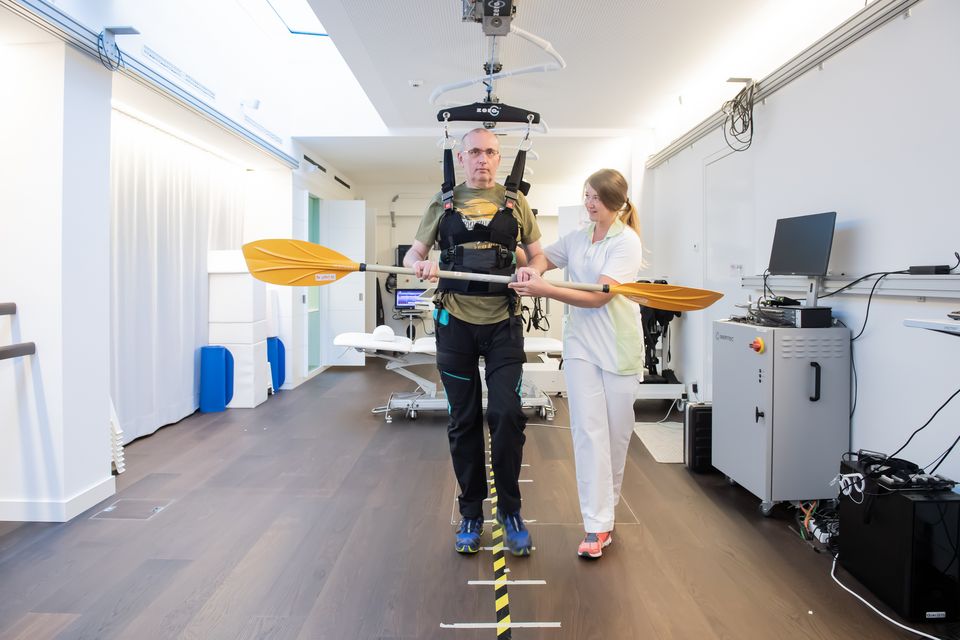
ZeroG® by Aretech
This innovative over-ground gait training tool helps to train mobility and balance. Dynamic partial body weight support (DBWS) reduces the risk of falling whilst offering the patient a real-life experience.
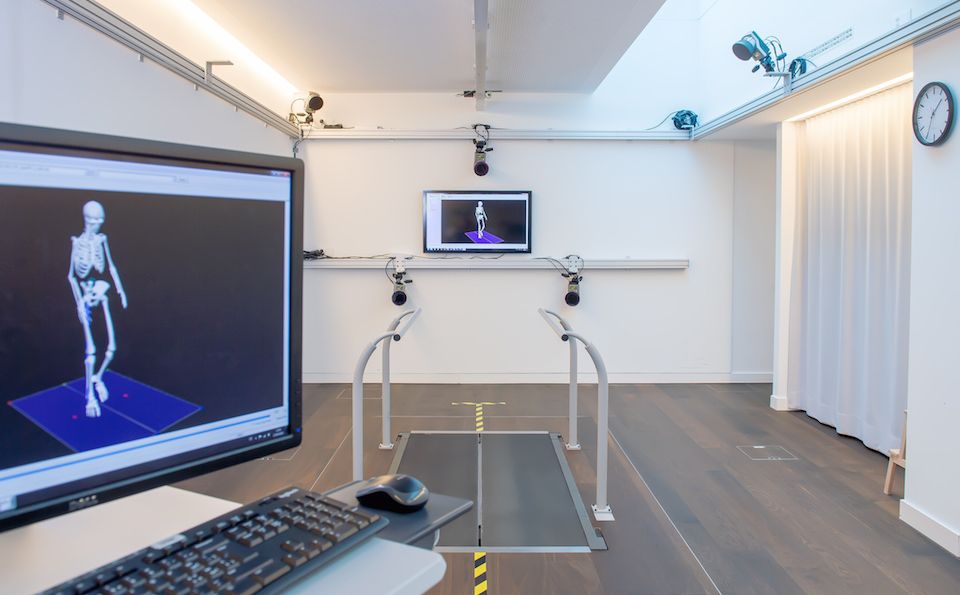

Split-belt treadmill
Training on a split-belt treadmill with different velocities for each limb can trigger brain adaptations that render the gait more symmetrical. After a stroke this can be used to make the gait faster and less exhausting.
Current stroke research projects
Together with the cereneo Institute for Interdisciplinary Research (cefir), the University Hospital of Zurich and the ETH (Technical University), we perform basic and clinical research including randomised controlled trials testing new training and diagnostic methods.








